Syndrome
 Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Legal, Financial, Acronyms, Idioms, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
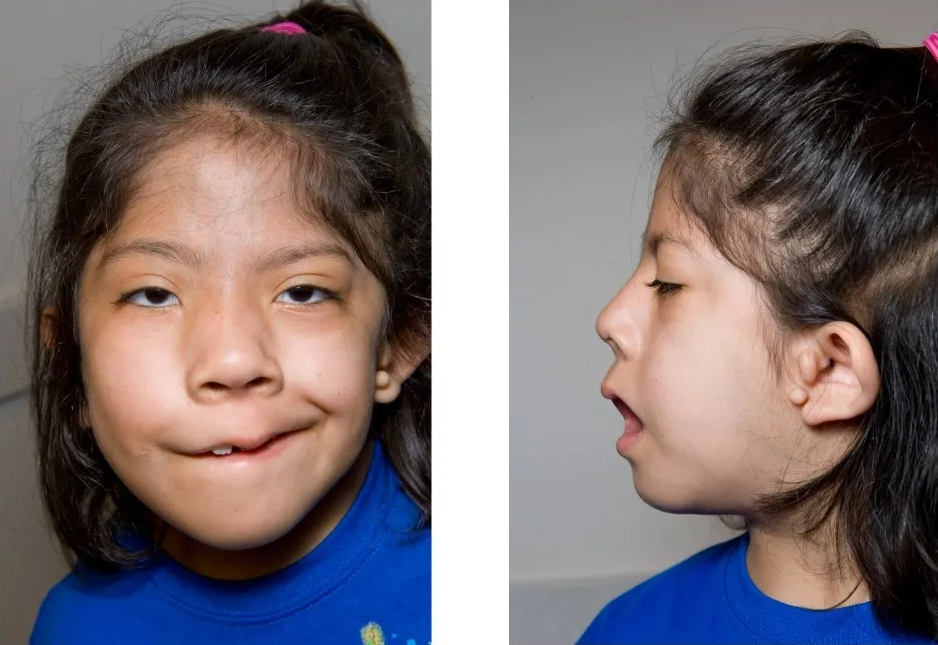
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Legal, Financial, Acronyms, Idioms, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.What is Usher syndrome? Usher syndrome is the most common condition that affects both hearing and vision; sometimes it also affects balance. The major symptoms of Usher syndrome are deafness or hearing loss and an eye disease called retinitis pigmentosa (RP) re-tin-EYE-tis pig-men-TOE-sa. Down syndrome is a genetic condition that causes mild to serious physical and developmental problems. People with Down syndrome are born with an extra chromosome. Chromosomes are bundles of genes.
syn·drome
(sĭn′drōm′)n.
syndrome
(ˈsɪndrəʊm) nsyn•drome
(ˈsɪn droʊm, -drəm)n.
syn·drome
(sĭn′drōm′)| Noun | 1. | syndrome - a complex of concurrent things; 'every word has a syndrome of meanings' complex, composite - a conceptual whole made up of complicated and related parts; 'the complex of shopping malls, houses, and roads created a new town' |
| 2. | syndrome - a pattern of symptoms indicative of some disease autism - (psychiatry) an abnormal absorption with the self; marked by communication disorders and short attention span and inability to treat others as people ADD, ADHD, attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, hyperkinetic syndrome, MBD, minimal brain damage, minimal brain dysfunction - a condition (mostly in boys) characterized by behavioral and learning disorders Horner's syndrome - a pattern of symptoms occurring as a result of damage to nerves in the cervical region of the spine (drooping eyelids and constricted pupils and absence of facial sweating) symptom - (medicine) any sensation or change in bodily function that is experienced by a patient and is associated with a particular disease cervical disc syndrome, cervical root syndrome - an abnormal condition resulting from compression of spinal nerve roots in the neck region; involves neck pains and muscular weakness and paresthesia Chinese restaurant syndrome - headache and tingling or burning feelings and sweating caused by eating food that contains monosodium glutamate Conn's syndrome - disturbances in saltwater balance and symptoms of weakness and muscular cramps and twitching and convulsions and sometimes paralysis; usually caused by a benign tumor of the cortex of the adrenal gland that leads to excess secretion of aldosterone FAS, fetal alcohol syndrome - a congenital medical condition in which body deformation occurs or facial development or mental ability is impaired because the mother drinks alcohol during pregnancy Gulf War syndrome, Persian Gulf illness - a medical condition of uncertain origin that affected many veterans of the 1991 Gulf War; characterized by fatigue and headache and dizziness and nausea and rashes and joint pain and respiratory disorders Klinefelter syndrome, Klinefelter's syndrome, XXY-syndrome - syndrome in males that is characterized by small testes and long legs and enlarged breasts and reduced sperm production and mental retardation; a genetic defect in which an extra X chromosome (XXY) is present in the male malabsorption syndrome - a pattern of symptoms including loss of appetite and bloating and weight loss and muscle pain and steatorrhea; associated with celiac disease and sprue and cystic fibrosis Munchausen syndrome, Munchausen's syndrome - syndrome consisting of feigning acute and dramatic illness for which no clinical evidence is ever found nephrosis, nephrotic syndrome - a syndrome characterized by edema and large amounts of protein in the urine and usually increased blood cholesterol; usually associated with glomerulonephritis or with a complication of various systemic diseases Noonan's syndrome - syndrome seen only in males; marked by short stature and lowset ears and subnormal fertility phantom limb syndrome - syndrome consisting of discomfort or pain in a limb that has been amputated PMS, premenstrual syndrome - a syndrome that occurs in many women from 2 to 14 days before the onset of menstruation radiation sickness, radiation syndrome, radiation - syndrome resulting from exposure to ionizing radiation (e.g., exposure to radioactive chemicals or to nuclear explosions); low doses cause diarrhea and nausea and vomiting and sometimes loss of hair; greater exposure can cause sterility and cataracts and some forms of cancer and other diseases; severe exposure can cause death within hours; 'he was suffering from radiation' Ramsay Hunt syndrome - syndrome resulting from infection by the herpes varicella zoster virus; characterized by vertigo and pain in the ears and facial nerve paralysis and sometimes hearing loss Reiter's disease, Reiter's syndrome - an inflammatory syndrome (etiology unknown) predominantly in males; characterized by arthritis and conjunctivitis and urethritis Ekbom syndrome, restless legs, restless legs syndrome - feeling of uneasiness and restlessness in the legs after going to bed (sometimes causing insomnia); may be relieved temporarily by walking or moving the legs Reye's syndrome - acquired encephalopathy following acute viral infections (especially influenza or chicken pox) in young children; characterized by fever, vomiting, disorientation, coma, and fatty infiltration of the liver scalenus syndrome - discomfort and vascular symptoms and loss of sensation in a shoulder and arm; caused by a scalene muscle compressing the subclavian artery and part of the brachial plexus apyretic tetanus, intermittent cramp, intermittent tetanus, tetanilla, tetany - clinical neurological syndrome characterized by muscular twitching and cramps and (when severe) seizures; associated with calcium deficiency (hypoparathyroidism) or vitamin D deficiency or alkalosis thoracic outlet syndrome - tingling sensations in the fingers; caused by compression on a nerve supplying the arm Tietze's syndrome - syndrome characterized by swelling of rib cartilage (causing pain) Gilles de la Tourette syndrome, Tourette's syndrome - neurological disorder characterized by facial grimaces and tics and movements of the upper body and grunts and shouts and coprolalia |
syndrome
syndrome
[ˈsɪndrəʊm]N → síndromemsyndrome
[ˈsɪndrəʊm]nsyndrome
syn·drome
n. síndrome, síntomas y señales que caracterizan una enfermedad;syndrome
n síndrome m; acquired immunodeficiency — (AIDS) síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida (SIDA or sida m); adult respiratory distress — (ARDS) síndrome de dificultad respiratoria del adulto (SDRA); antiphospholipid — síndrome antifosfolípido; apical ballooning — síndrome de discinesia apical (transitoria); Asherman's — síndrome de Asherman; bacterial overgrowth — sobrecrecimiento bacteriano intestinal; battered child — síndrome del niño maltratado; blind loop — síndrome de(l) asa ciega; broken heart — síndrome del corazón roto; carcinoid — síndrome carcinoide; carpal tunnel — síndrome del túnel carpiano; chronic fatigue — síndrome de fatiga crónica; Churg-Strauss — síndrome de Churg-Strauss; compartmental — síndrome compartimental; complex regional pain — síndrome de dolor regional complejo; Cushing's — síndrome de Cushing; Down — síndrome de Down; Ehlers-Danlos — síndrome de Ehlers-Danlos; empty nest — síndrome del nido vacío; Felty's — síndrome de Felty; fetal alcohol — síndrome alcohólico fetal; Gilbert's — síndrome de Gilbert; Gilles de la Tourette — síndrome de Gilles de la Tourette; Guillain-Barré — síndrome de Guillain-Barré; hemolyticuremic — síndrome hemolítico-urémico; hepatorenal — síndrome hepatorrenal; irritable bowel — síndrome de(l) intestino irritable, síndrome de(l) colon irritable; Klinefelter — síndrome de Klinefelter; Marfan — síndrome de Marfán; metabolic — síndrome metabólico; Munchausen — síndrome de Munchausen; myelodysplastic — síndrome mielodisplásico; nephrotic — síndrome nefrótico; neuroleptic malignant — síndrome neuroléptico maligno; obesity-hypoventilation — síndrome de hipoventilación por obesidad; Osler-Weber-Rendu — síndrome de Osler-Weber-Rendu; overactive bladder — síndrome de vejiga hiperactiva; overuse — síndrome de sobrecarga, lesión f por sobrecarga (esp. Esp); Peutz-Jeghers — síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers; Pickwickian — (ant) síndrome de hipoventilación por obesidad, síndrome de Pickwick (ant); polycystic ovary — síndrome de ovario poliquístico; postcon-cussion — síndrome postconmocional; post-polio — síndrome post-polio; premenstrual — (PMS) síndrome premenstrual (SPM); Reiter's — (ant) artritis reactiva, síndrome de Reiter (ant); restless legs — síndrome de piernas inquietas; Reye's — síndrome de Reye; severe acute respiratory — (SARS) síndrome respiratorio agudo severo (SRAS); Sheehan's — síndrome de Sheehan; short bowel — síndrome de intestino corto; Sjögren's — síndrome de Sjögren; staphylococcal scalded skin — síndrome de la piel escaldada estafilocócica; Stevens-Johnson — síndrome de Stevens-Johnson; sudden infant death — (SIDS) síndrome de muerte súbita del lactante or infantil; toxic shock — síndrome de choque tóxico; Turner — síndrome de Turner; wasting — síndrome de desgaste; Wernicke-Korsakoff — síndrome de Wernicke-Korsakoff; Wolff-Parkinson-White — síndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-WhiteWant to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.

Link to this page:
SYNDROMES
ENVIRONMENTAL CAUSES
- ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Radiation exposure.
- 12 hours post-exposure: Vomiting
- 24 hours post-exposure: Prostration (extreme exhaustion), fever, diarrhea
- Later: Petechial hemorrhage, hypotension, tachycardia, profuse bloody diarrhea, maybe death.
- CHINESE RESTAURANT SYNDROME:MSG reaction ------> Chest Pain, burning sensation over parts of body.
- BROWN-SEQUARD SYNDROME: Damage (injury) to half of spinal cord ------> symptoms:
- Loss of pain and temperature sensation on contralateral side of body.
- Loss of proprioception and discriminatory touch on ipsilateral side of body.
CARDIOVASCULAR
- ADAMS-STOKES SYNDROME: Heart block, with slow or absent pulse, often accompanied by convulsions.
- BARLOW SYNDROME:Floppy Mitral Valve Syndrome; Massive Mitral Valve Prolapse ------> Late apical systolic murmur, systolic click, or both.
- EISENMENGER'S SYNDROME: Ventricular-Septal Defect ------> Pulmonary hypertension and cyanosis.
- FLOPPY-VALVE SYNDROME:Mitral Incompetence due to myxomatous degeneration of the leaflets.
- LERICHE'S SYNDROME:Occlusion of distal aorta ------>
- Hip, thigh, and calf fatigue.
- Impotence
- BEHCET'S SYNDROME:Vasculitis ------> secondary symptoms:
- Oral and genital ulcers
- Uveitis
- Optic atrophy
- SHOULDER-HAND SYNDROME: Pain in shoulder and swelling in hand, sometimes occurring after Myocardial Infarction.
- SICK SINUS SYNDROME:Chaotic atrial activity; continual changes in P-Waves. Bradycardia, alternating with recurrent ectopic beats and runs of tachycardia.
- SUPERIOR VENA CAVA SYNDROME: Caused by a tumor. Obstruction of SVC ------>
- Edema
- Engorgement of the vessels of face, neck, and arms.
- Nonproductive cough
- Dyspnea
- TAKAYASU'S SYNDROME: Arteritis of the Aortic Arch, resulting in no pulse. Seen in young women.
- WOLF-PARKINSON WHITE SYNDROME: ECG pattern of Paroxysmal Tachycardia.
- Short PR interval
- Delta wave = early QRS complex.
IATROGENIC (or Secondary to Medical Treatment)
- AFFERENT LOOP SYNDROME: Gastrojejunal loop obstruction, proximal to a gastrojejunostomy.
- Ingestion of food produces nausea, pain, and duodenal distension.
- ASHERMAN'S SYNDROME:Adhesions within the endometrial cavity, causing amenorrhea and infertility.
- Adhesions probably were caused by surgery.
- ULYSSES SYNDROME: Ill effects from follow-up diagnostic tests following a false-positive screening test.
NEOPLASTIC (Malignant or Benign)
- CARCINOID SYNDROME: Carcinoid tumor producing Bradykinin + Serotonin ------> secondary symptoms:
- Cyanotic flushing
- Bronchial spasm
- Edema, ascites.
- CRONKHITE-CANADA SYNDROME:GI-Polyps with diffuse alopecia (hair-loss) and nail dystrophy.
- May see protein-losing enteropathy and malabsorption.
- GARDNER'S SYNDROME: Multiple inherited tumors, hereditary dominant trait.
- Skull osteomas, Fibromas, Epidermoid cysts
- Colonic polyposis (APC gene) ------> predisposition to colonic adenocarcinoma.
- LAMBERT-EATON SYNDROME: Progressive proximal muscle weakness secondary to a carcinoma.
- MEIGS' SYNDROME:Fibroma of ovary with ascites and hydrothorax
- PANCOAST SYNDROME:Tumor near pulmonary apex ------>
- Neuritic pain of chest and arm
- Muscle atrophy of the arm
- Horner's Syndrome (impaired cervical sympathetics)
- PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME: Polyposis (hamartomas) of small intestine
- Also see melanin pigmentation of buccal mucosa and skin around mouth and lips
CONGENITAL
- CEREBELLAR SYNDROME:Congenital Cerebellar Ataxia
- CERVICAL SYNDROME:Supernumerary C7 rib ------> Pressure on brachial plexus ------> pain radiating over shoulder, arm, and forearm over C7 distribution.
- DANDY-WALKER SYNDROME:Obstruction of Foramina of Magendie and Luschka in infants ------> Hydrocephalus.
- DIGEORGE SYNDROME:Congenital absence of 3rd and 4th Branchial Arches (Thymus and Parathyroid Glands) ------> secondary symptoms:
- No cell-mediated immunity ------> Frequent viral and fungal infections
- Characteristic facial deformities
- DOWN SYNDROME:Trisomy 21. Mental retardation, characteristic facial features, Simeon crease in hand.
- FANCONI'S SYNDROME Type I:Bone-marrow hypoplasia ------> refractory anemia, pancytopenia.
- EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME: Congenital defect in collagen.
- Hyper-elasticity and friability of the skin.
- Hyperextensibility of the joints.
- FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME: Fetal malformations, growth deficiencies, craniofacial anomalies, limb defects.
- GOODPASTURE'S SYNDROME: Autoantibodies against basement membranes ------> Glomerulonephritis (kidney) and hemoptysis (lungs).
- Often, death by renal failure
- KLINEFELTER'S SYNDROME: Trisomy XXY ------> testicular atrophy, increase in gonadotropins in urine.
- KLIPPEL-FEIL SYNDROME:
- Cervical vertebrate fused
- Congenital short neck, limited neck rotation
- Abnormalities of the brainstem and cerebellum
- Low hairline.
- LESCH-NYHAN SYNDROME:Deficiency of HGPRT (Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phospho-ribosyltransferase ------>
- Hyperuricemia, uric acid kidney stones
- Choreoathetosis
- Mental retardation, autism, spastic cerebral palsy
- X-Linked recessive
- MARFAN SYNDROME: Connective Tissue disorder ------>
- Arachnodactyly: Abnormally long digits and extremities
- Subluxation of lens
- Dissecting aortic aneurism
- POSTRUBELLA SYNDROME: Infantile defects resulting from maternal Rubella infection during first trimester.
- Microphthalmos, cataracts
- Deafness
- Mental retardation
- Patent ductus arteriosis, Pulmonary arterial stenosis
- PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME: Short stature, mental retardation, polyphagia with marked obesity, sexual infantilism.
- RENDU-OSLER-WEBER SYNDROME:Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
- SUDDEN INFANT DEATH SYNDROME: Unexplained death in sleeping infants.
- TURNER'S SYNDROME: XO monosomy.
- Dwarfism
- Webbed neck
- Valgus of elbow.
- Amenorrhea
- WILSON SYNDROME: Congenital defect in Ceruloplasmin, leading to buildup of copper ------> mental retardation, cirrhosis, hepatolenticular degeneration.
ENDOCRINE, REPRODUCTIVE
- AMENNORRHEA-GALACTORRHEA SYNDROME:Non-physiologic lactation, resulting from endocrinologic causes or from a pituitary disorder.
- CONN'S SYNDROME: Primary Hyperaldosteronism ------> muscular weakness, hypertension, hypokalemia, alkalosis.
- CUSHING'S SYNDROME:Hypersecretion of cortisol ------> secondary symptoms and characteristics:
- Fatness of face and trunk with wasting of extremities
- Buffalo hump
- Bone decalacification
- Corticoid diabetes
- Hypertension
- PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME: Abnormal sensation in breasts, abdominal pain, thirst, headache, pelvic congestion, nervous irritability.
- Ocassionally nausea and vomiting.
- SHEEHAN'S SYNDROME:Post-partum pituitary necrosis ------> hypopituitarism.
- STEIN-LEVENTHAL SYNDROME:Polycystic ovary ------> infertility, amenorrhea, hirsutism. Seen in obese women.
- TESTICULAR FEMINIZATION SYNDROME: Insensitivity to Testosterone. Male Psuedohermaphroditism
- Complete female external genatalia, incompletely developed vagina, rudimentary uterus.
PULMONARY
- KARTAGENER'S SYNDROME:Situs Inversus (lateral transposition of lungs) resulting from chronic sinusitis and bronchiectasis.
- HAMMAN-RICH SYNDROME:Interstitial fibrosis of the lung.
- MIDDLE-LOBE SYNDROME: Chronic pneumonitis and atalectasis of middle lobe of right lung.
- CHURG-STRAUSS SYNDROME:Allergic Granulomatous Angiitis: Asthma, fever, eosinophilia.
INFECTIOUS
- FITZ-HUGH-CURTIS SYNDROME:Gonococcal Periphepatitis in woman, as a complication of Gonorrhea.
- GUILLAIN-BARRE SYNDROME:Infectious Polyneuritis of unknown cause.
- HUNT'S SYNDROME: Herpe's Zoster infection of Facial Nerve (CN VII) and Geniculate Ganglion ------> facial palsy.
- Zoster of ear
- PARINAUD'S SYNDROME: Preauricular lymph node enlargement on the same side as conjunctivitis.
- REYE'S SYNDROME: Loss of consciousness and seizures in kids, after a viral infection treated by aspirin.
- REITER'S SYNDROME: Symptom cluster. Etiology is thought to be Chlamydial or post-chlamydial.
- Urethritis
- Iridocyclitis (Conjunctivitis)
- Arthritis
- Skin lesions like karatoderma blenorrhagicum
- Also can see fatty liver or liver necrosis.
- SCALDED SKIN SYNDROME:S. Aureus toxic epidermal necrolysis.
- STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME:Erythema Multiformecomplication.
- Large areas of skin slough, including mouth and anogenital membranes.
- Mucous membranes: stomatitis, urethritis, conjunctivitis.
- Headache, fever, malaise.
- TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME: Caused by superabsorbent tampons. Infection with Staph Aureus and subsequent toxicity of exotoxin TSST ------> systemic anaphylaxis.
- Fever, vomiting, diarrhea
- Red rash followed by desquamation
- WATERHOUSE-FRIEDRICHSON SYNDROME:Meningeococcal Meningitis ------> DIC, hemorrhagic infarct of adrenal glands ------> fulminant adrenal failure.
- Vomiting, diarrhea.
- Shock
- Extensive purpura, cyanosis, circulatory collapse.
RENAL
- KEMMELSTIEL-WILSON SYNDROME:Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis.
- BARTTER'S SYNDROME: Juxtaglomerular Cell Hyperplasia ------> secondary symptoms:
- Hyperaldosteronism, Hypokalemic Alkalosis, elevated renin and angiotensin
- No hypertension.
- Compare to Conn's Syndrome
- FANCONI'S SYNDROME Type II: Renal aminoaciduria, glycosuria, hypophosphaturia, cysteine deposition, rickets.
- THORN'S SYNDROME:Salt-losing nephritis.
NEUROLOGICAL
- CARPAL-TUNNEL SYNDROME:Compression of Median Nerve through the Carpal Tunnel ------> pain and parasthesia over distribution of Median N.
- FROIN'S SYNDROME:Block in CSF flow ------> xanthochromia (yellow discoloration) of CSF.
- ACUTE-BRAIN SYNDROME: Delirium, confusion, disorientation, developing suddenly in a person that was previously psychologically normal.
- GERSTMANN'S SYNDROME:Lesion between occipital area and angular gyrus ------> symptoms:
- Finger agnosia, Agraphia, acalculia
- Right-left disorientation
- HORNER'S SYNDROME:Loss or lesion of cervical sympathetic ganglion ------>
- Ptosis, miosis, anhydrosis
- Enophthalmos (caved in eyes)
- KORSAKOFF SYNDROME: Loss of short-term memory in chronic alcoholism, caused by degeneration of mamillary bodies.
- RILEY-DAY SYNDROME:Familial dysautonomia.
GASTROINTESTINAL
Syndrome Meaning
- MALLORY-WEISS SYNDROME: Laceration of lower end of esophagus from vomiting ------> hematemesis. Often seen in alcoholics.
- MALABSORPTION SYNDROME: Impaired absorption of dietary substance ------> diarrhea, weakness, weight loss, or symptoms from specific deficiencies.
- BARRETT SYNDROME: Chronic peptic ulcer of the lower esophagus, resulting in metaplasia of esophageal columnar epithelium ------> squamous epithelium.
- ZOLLINGER-ELLISON SYNDROME:Gastrin-secreting tumor in pancreas ------> Severe peptic ulcers, gastric hyperacidity.
- PLUMMER-VINSON SYNDROME: Esophageal Webs, leading to dysphagis and atrophy of papillae of tongue.
- Also see hypochromic anemia, splenomegaly.
RETICULOENDOTHELIAL, HEMATOLOGIC
- BANTI'S SYNDROME:Chronic Congestive Splenomegaly with anemia, caused by either Portal Hypertension or Splenic Vein Thrombosis.
- BUDD-CHIARI SYNDROME:
- ACUTE: Hepatic Vein Thrombosis ------> Massive ascites and dramatic death.
- CHRONIC: Gradual hepatomegaly, portal hypertension, nausea, vomiting, edema, ulimately death.
- DUBIN-JOHNSON SYNDROME:Defect in excretion of conjugated bilirubin ------> recurrent mild jaundice. Buildup of direct builirubin in blood.
- CHIDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROME:Abnormalities in leukocytes with large inclusions.
Syndrome Incredibles
- CRUVEILHIER-BAUMGARTEN SYNDROME: Symptoms cluster:
- Liver cirrhosis
- Caput Medussae
- Venous hum and thrill
- FELTY'S SYNDROME: Rheumatoid Arthritis with splenomegaly, leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia.
- LOFFLER'S SYNDROME:Eosinophilia with transient infiltrates in lungs.
- PARINAUD'S SYNDROME: Preauricular lymph node enlargement on the same side as conjunctivitis.
UNCATEGORIZED
- YELLOW-NAIL SYNDROME: Stop growth of nails ------> increased convexity, thickening, and yellowing of nails.
- Found in Lymphedema, bronchitis, chronic bronchiectasis.
- COSTOCHONDRAL SYNDROME: Pain in chest with tenderness over one or more costochondral junctions.
- Similar to Tietze's Syndrome but no specific inflammation.
- TIETZE'S SYNDROME: Costochondritis. Swelling and tenderness of the costal cartilege.
- MIKULICZ'S SYNDROME:Salivary and lacrimal enlargement as seen in several diseases:
- Sarcoidosis
- Tuberculosis
- Leukemia
- MUNCHAUSEN SYNDROME:Malingering -- fabrication of a clinically convincing disease by an itinerant malingerer.
- PICKWICKIAN SYNDROME: Symptom cluster
- Obesity
- Hypoventilation
- Somnolence
- Erythrocytosis
- RESTLESS LEGS SYNDROME: Need to stretch legs at night before going to sleep; twitch in legs causing insomnia.
- STRAIGHT BACK SYNDROME:Loss of normal kyphosis of thoracic spine ------>
- Straight spine
- Ejection murmur
- Widened cardiac silouhette on x-ray
- SJ?REN'S SYNDROME: Autoimmune complex
- Keratoconjuctivitis Sicca (dry eyes and mouth)
- Dryness of Mucous membranes
- Telangiectasias in face
- Parotid enlargement
Copyright ©1999, Scott Goodman, all rights reserved
Are you a Doctor, Pharmacist, PA or a Nurse?
Join the Doctors Lounge online medical community
Editorial activities: Publish, peer review, edit online articles.
Ask a Doctor Teams: Don't starve together: all survivors gorge chest. Respond to patient questions and discuss challenging presentations with other members.